The unicellular and multicellular organisms are different from each other because of the number of cells. So, these cells cause a change in structure, function, and shape. A unicellular organism performs its daily task with a single cell, but multicellular organisms have many types of cells which perform specific functions. Here we have a chart that shows the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms so you can understand it easily.
| Comparison Basis | Unicellular | Multicellular |
| definition | Unicellular organisms are composed of one types | Multicellular organisms are made up of many kinds of cells or more than one cell. |
| Body Formation | Body formation is elementary. | Therefore, Body formation is complicated and tricky. |
| Body visible | All body cells are visible to the environment. | Only outer cells are visible to the environment. |
| Division of cells | The division of cells is organelle but in level. | The division of different type of cells make tissues, organelles, organs system but in level. |
| Movement of material | Because simple methods are used to carry materials. | The simple diffusion method and active and passive transport are used as a movement of materials. |
| Organism include | Include both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. | Only eukaryotes. |
| Life cycle | The life cycle is concise. | Have a long life cycle. |
| Case of accident injury | In case of any injury or wound that causes the death of an organism. | However, The injury or wound may not cause the death of the organism. |
| Cell division | Asexual cell division is present. Similarly, maybe conjugation is present.
Mitosis is present. |
Both sexual and asexual cell division is present.
Mitosis and meiosis is present. |
Size |
Very small ( can be seen only in the microscope) | Large in size After that macroscopic nature. |
| Cell differentiation | Cell differentiation is absent because it has only one type of cell. | Cells can be differentiated because more than one cells are present. |
| Life process | Organisms have a simple but life process. | So many cells perform different functions. |
| Shape | Have an irregular but straightforward shape. | Have a well-defined shape. |
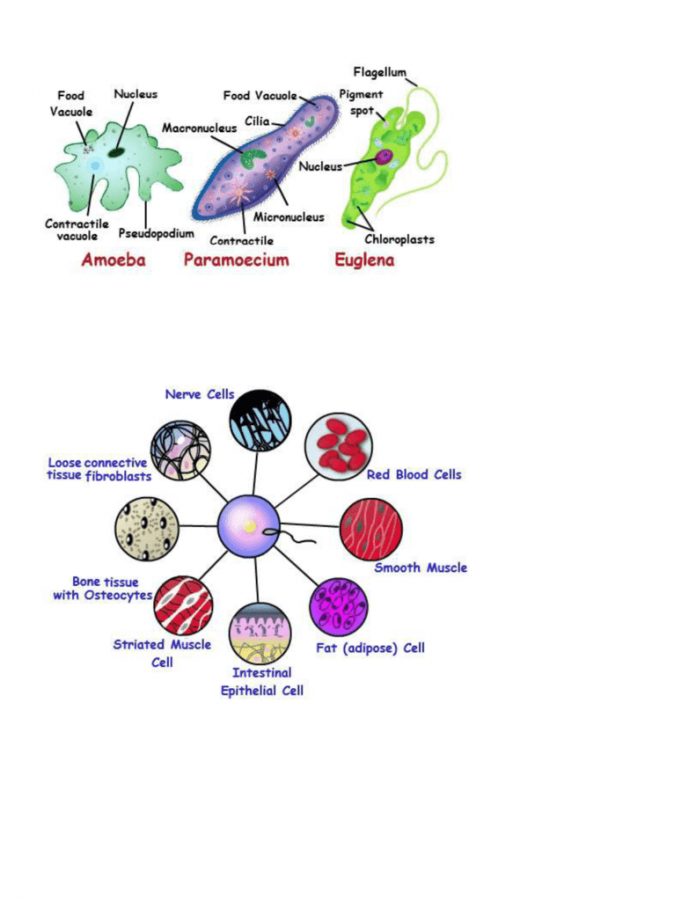
| Examples | Bacteria, amoeba, paramecium, euglena, yeast, etc. So are unicellular organisms. | Humans, animals, plants, birds, and For instance, insects are multicellular organisms. |
Unicellular Organisms
So, the unicellular organisms are single-cell organisms, and fossils show that they are the first living organisms on earth. These organisms are tiny. The naked eye can’t see that, so they are called microscopic animals. So, we have an asexual reproduction binary fission, fragmentation, and sometimes sexual by conjugation. But, they have a simple and irregular body. So, they include prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Examples: amoeba, euglena, plasmodium, euglena, paramecium, algae, fungi, etc
Multicellular Organism
Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell and are called living organisms. They have different cells which make other organs, so they perform different complex functions. They are macroscopic so that they can be seen quickly by the naked eye and observed well. These organisms reproduce by both sexual and asexual reproduction by spore formation, budding. And asexual reproduction is present in plants. So the size of an organism increases as the cell size increases.
Examples: plants, animals, human beings.
Also read: Difference between heat and temperature.